圣母院大学和印第安纳大学医学院的科学家对酒精性脂肪肝进行研究,揭示了肝细胞生物钟与这种疾病的潜在关联。相关文章发表于2014年1月16日的《Scientific Reports》杂志上。
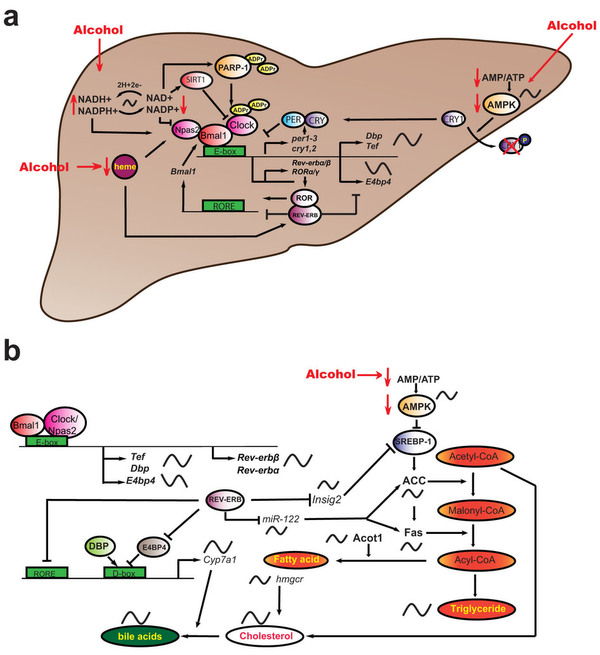
酒精性脂肪肝会破坏肝细胞生物钟进而推动脂肪肝进一步发展
脂肪肝(Hepatic steatosis)是指肝细胞中出现了异常的脂肪累积,这通常是由于肝脏的脂肪代谢受到了破坏。过度饮酒会引起酒精性脂肪肝,进而发展成为更为严重的疾病,例如肝炎或者肝硬化。在长期大量饮酒的人中,10%到35%会患上酒精性的肝炎,这种疾病也是西方国家中的主要肝病类型。
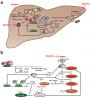
为了深入研究酒精性脂肪肝,研究人员建立了长期饮酒(四周)并发生肝脏脂肪变性的小鼠模型。他们发现,在酗酒引起肝脏病变的同时,肝脏细胞的正常生物钟系统也受到破坏。更重要的是,这种肝细胞的生物钟紊乱,独立于大脑中的生物钟系统。
生物钟负责调解机体和细胞的生化、生理和行为节律。生物钟的正常运作需要与外部世界正确同步(特别是昼夜循环交替),这对于机体的健康状态非常关键。研究人员指出,生物钟紊乱与精神疾病、代谢性疾病(包括肥胖和糖尿病)甚至癌症的发展有关。
肝脏在机体中负责许多重要的功能,包括调控代谢、储存和释放能量分子以及解毒作用。“肝脏功能在一天中的节律性改变,应该与进食行为和机体的能量需求相协调。举例来说,我们活动和休息时需要的能量不同。” Notre Dame大学的副教授Giles Duffield说,他与Indiana大学的Suthat Liangpunsakul共同领导了这项研究。“这些节律性变化受到肝细胞生物钟的调控,如果调控机制受到破坏就会引发疾病。”
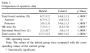
为此,研究人员深入研究了脂肪肝对肝细胞生物钟的影响。他们发现,在酒精性脂肪肝的小鼠模型中,生物钟基因和生物钟调控基因的表达发生了改变。此外,甘油三酯、胆固醇、胆汁酸,以及NAD/NADH的节律性合成也发生了改变,而这些物质都是生物钟调控的基础。
研究人员强调,在酒精诱导的脂肪肝中,控制节律的生物钟系统受到干扰,而这种影响会进一步推动脂肪肝的发展。这一发现,无疑为治疗相关疾病带来了新的宝贵线索。
原文摘要:
Disturbances in the murine hepatic circadian clock in alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis
Peng Zhou, Ruth A. Ross, Cameron M. Pywell, Suthat Liangpunsakul & Giles E. Duffield
To investigate the role of the circadian clock in the development of alcohol-induced fatty liver disease we examined livers of mice chronically alcohol-fed over 4-weeks that resulted in steatosis. Here we show time-of-day specific changes in expression of clock genes and clock-controlled genes, including those associated with lipid and bile acid regulation. Such changes were not observed following a 1-week alcohol treatment with no hepatic lipid accumulation. Real-time bioluminescence reporting of PERIOD2 protein expression suggests that these changes occur independently of the suprachiasmatic nucleus pacemaker. Further, we find profound time-of-day specific changes to the rhythmic synthesis/accumulation of triglycerides, cholesterol and bile acid, and the NAD/NADH ratio, processes that are under clock control. These results highlight not only that the circadian timekeeping system is disturbed in the alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis state, but also that the effects of alcohol upon the clock itself may actually contribute to the development of hepatic steatosis.