第十三章 生殖
2011-06-08 18:30:32 来源: 作者: 评论:0 点击:
Summary
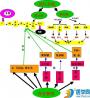
The physiology of the reproduction is to produce offspring. The process of reproduction includes fertilization, pregnancy and delivery. Reproduction is modulated by the neuroendocrine system of hypothalamus-adenohypophysis-testes axis.
The testes must descend out of the abdomen to function properly. Spermatozoa are produced by mitosis, followed by meiosis, and then followed by spermiogensis. The main hormones of spermatogenesis are LH, testosterone, and FSH, together with several auxillary hormones.
The first half of the ovarian cycle involves follicular development which is estrogen-dominated and is separated by a short ovulatory phase from the progesterone-dominated second half which prepares the uterus for implantation. All of a woman's primary oocytes (2 million) are present at birth; no more are made. The ovarian cycle consists of one of the several follicles developing into a primary follicle, then Graafian follicle, then a corpus luteum under the influences of FSH and LH. Ovulation is triggered by a powerful surge of gonadotrophins.The ovarian cycle is "shadowed" by the menstrual cycle during which the uterine endometrium is firstly proliferative (due to estrogen) then secretory (due to estrogen and progesterone). Decline in progesterone and estrogen when the corpus luteum degenerates precipitates a menstruation.
Human pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, divided into three trimesters. Only 1 per 100,000 sperm of the 200~400 million contained in the 3~4 ml of the ejaculation deposits near the cervix, where capacitation takes place, reach the fallopian tubes where fertilization ideally occurs. Enzymes from the acrosomes of the many sperm digest the intercellular cement between the cumulus cells, allowing a single sperm to penetrate. On penetration by the first sperm, the ovum becomes impervious to other sperm. A second polar body is released. About 6 days after fertilization, the zygote (now a blastocyst) implants. The placenta takes over the production of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum after the first trimester of the pregnancy. Placenta progesterone inhibits inappropriate contractions of the myometrium. Labor is divided into three phase: first-from onset of contractions to full dilatation of the cervix; second-to delivery of the fetus; third-the expulsion of the placenta.
(中山大学中山医学院 周灿权 王庭槐)
参考文献
1.徐丰彦,张镜如主编.1989. 人体生理学.第二版. 北京:人民卫生出版社.
2.姚泰,罗自强主编.2001. 生理学.第五版.北京:人民卫生出版社.
3.吴阶平编译. 1982. 性医学. 北京:科学技术文献出版社.
4. 陈大元.2000. 受精生物学.北京:科学出版社.
5. Fox SI. 2002. Human Physiology. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Co.
6. Davies A,Blakeley AGH,Kidd C. 2001. Human Physiology. London:Harcourt Publishers Ltd.
7. Berne RM. 1996. Principles of Physiology. 2nd ed. St. Louis:Mosby.
8. Ganong WF. 1999. Review of Medical Physiology, 19th ed. Stamford:Appleton & Lange.
9.Longstaff A. 2000. Instant Notes in Neuroscience. Oxford:Bios Scientific Pub Ltd.
复习参考题
1.男性的生殖功能具有哪两个功能,有什么特点?
2.精子发育成熟要经历哪几个阶段?
3.睾丸能分泌何种激素,简述男性激素的生理功能。
4.睾丸的生精过程受哪些激素调节?
5.简述受精的过程。
6.简述雌激素分泌的双重细胞学说及雌激素分泌的调节。
7. 简述妊娠的生理过程,妊娠的维持和激素调节。
8. 比较睾丸与卵巢功能调节的特点。
9. 运用所学的知识,设计安全避孕的方法并解释其原理。
相关热词搜索:生殖
上一篇:第十二章 内分泌系统
下一篇:最后一页
精彩图文
论坛新帖
频道总排行
医学推广
频道本月排行
- 18第十章 感觉器官的功能
- 18第五章 呼吸
- 16第六章 消化和吸收
- 13第二章 细胞的基本功能
- 10第十一章 神经系统
- 7第一章 绪论
- 4第三章 血液
- 3第七章 能量代谢
- 2第四章 血液循环
- 1第十三章 生殖
热门购物
评论排行
- 2011年临床执业医师考试实践技能真...(13)
- 腋臭手术视频(11)
- 2008年考研英语真题及参考答案(5)
- 节食挑食最伤女人的免疫系统(5)
- 核辐射的定义和单位(5)
- CKD患者Tm与IMT相关(5)
- 齐鲁医院普外科开展“喉返神经监护...(5)
- windows7激活工具WIN7 Activation v1.7(5)
- 正常微循环(5)
- 美大学性教育课来真的 男女上阵亲...(4)