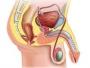
肥胖也会影响男性的性功能及泌尿系健康
2012-08-04 21:12:42 来源: 丁香园 作者: 评论:0 点击:
丁香园 作者: 评论:0 点击:
As a man's waistline grows, so can his experience with sexual dysfunction and frequent urination, say researchers at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. The study, published in the August issue of the British Journal of Urology International (BJUI), is the first to comprehensively show that obesity in men affects not just their hearts and metabolism, but also their sexual and urinary health.
纽约Presbyterian医院/ Weill Cornell医疗中心的研究人员称,随着男性腰围的增长,其可能更常出现性功能障碍及尿频。这篇发表于8月出版的不列颠国际泌尿学杂志的(BJUI)研究,首次全面显示了男性肥胖不仅对其心脏及代谢方面,还对其性及泌尿健康存在影响。
"The findings demonstrate that obesity in men -- part of a growing global epidemic -- affects their well-being in profound ways," says the study's senior investigator Dr. Steven A. Kaplan, the E. Darracott Vaughan Jr., Professor of Urology at Weill Cornell Medical College, director of the Iris Cantor Men's Health Center and chief of the Institute for Bladder and Prostate Health at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell.
纽约Presbyterian/Weill Cornel膀胱与前列腺健康研究所及Iris Cantor男性健康中心主任、Weill Cornell医学院泌尿科学教授小E. Darracott Vaugha以及本研究的高级研究员Steven A. Kaplan博士指出:“结果表明男性肥胖——作为增长中的全球流行病的一部分,在深层影响着他们的健康。”
"We have to think of the body in a much more holistic way. What we eat can have devastating consequences on more than just our hearts," Dr. Kaplan says. "Quality of life issues, such as sexual and voiding health, can be affected as well in drastic ways."
“我们不得不从一种更整体的角度思考机体。我们的所吃下的食物可能不仅仅对心脏产生破坏性的后果,”Kaplan博士指出,“生活质量方面,如性和排泄方面的健康,也有可能受到严重影响。”
The study also suggests that losing weight can help men overcome these issues that previously were not directly linked to body mass, Dr. Kaplan adds. In fact, additional findings conducted since this study was completed show that eliminating just 2.5 inches from the belly's circumference may lead to measurable improvement in sexual dysfunction and frequent urination, he says.
Kaplan博士补充,该研究还显示减肥可以帮助男性克服上述之前并不(认为)与体重直接相关的问题。事实上,该研究结束后的进一步(研究)结果显示,腹围仅减少2.5英寸就会使性功能障碍及尿频的情况获得显著的改善。”
The findings now offer physicians an easy metric to gauge which male patients might be experiencing sexual or urologic dysfunction, the researchers say.
研究人员称:已获得结果可以为医生提供一种简便的评价可能会有性或排尿障碍的男性患者的测量方法。
"Measuring a man's waistline is easy, noninvasive and does not require extensive testing," Dr. Kaplan says.
Kaplan博士说:“测量腰围简便、无创,并不需要繁琐的检查。”
Largest Waist Size Linked to Many Health Issues
最大腰围与许多健康问题相关
The research team studied 409 men diagnosed with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) at the Institute for Bladder and Prostate Health at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell. The goal of the study was to see if obesity was linked to LUTS, a common problem affecting older men. LUTS symptoms include difficulty urinating, such as increased frequency during the day and night. Previous smaller studies have suggested body weight could be linked to LUTS, but this new study was designed to be the most definitive and comprehensive to date, Dr. Kaplan says.
Of the participants enrolled in the study ranging from 40-91 years of age, 37.5 percent had a waist circumference of less than 36 inches, 33.5 percent of men had waists that were between 36-40 inches, and 29 percent of men had waists greater than 40 inches.
研究人员选取了409例来自于纽约Presbyterian/Weill Cornel膀胱与前列腺健康研究所的诊断为有下尿路症状的男性。研究目的为观察肥胖是否和经常困扰老年男性的下尿路症状相关。下尿路症状包括:排尿困难,如昼夜排尿次数增加。Kaplan博士称:之前小样本的已表明体重可能与下尿路症状相关,但本次则为迄今最确切和最广泛的研究。
The investigators found that a larger waist size was linked to more frequent urination: 39 percent of men with the biggest waistlines urinated more than eight times in 24 hours, compared to 27 percent of men in the middle range and 16 percent of men with the smallest waists. The same patterns were seen for nighttime urination: 44 percent of men with the biggest waists had to urinate more than twice at night, compared to 29 percent of men in the middle-sized group, and 15 percent of the slimmer men. The researchers also surveyed the participants about their sexual health and found that 74.5 percent of men with the largest waists reported erectile dysfunction, compared with 50 percent of men in the middle group and 32 percent of men with the smaller waists. Ejaculation problems followed the same pattern - 65 percent, 40 percent, and 21 percent, respectively.
研究人员发现腰围越大,尿频出现越多:最大腰围组的男性中39%(平均)24小时排尿8次以上,对比看来,这在中度腰围组有27%,最小腰围组仅为16%。在夜尿方面也有类似的情况:最大腰围组的男性中的44%出现夜尿两次以上,而这(仅)出现于29%的中度腰围组男性及15%的节食减肥者。研究人员还调查了研究对象的性健康情况并发现最大腰围组的男性中74.5%报告存在勃起障碍,对比中度及较小腰围组出现上诉情况的仅占各组的50%和32%。射精问题存在相似的情况,分别占各组的65%,40%及21%。
To provide a comprehensive view of health issues associated with waist circumference, the research team also assessed other variables linked to obesity. In the study, high blood pressure, cholesterol, coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes were more prevalent in men with larger waist sizes.
研究组还评估了与肥胖相关的其他变量,得出了与腰围相关健康问题的全面观点。在研究中,在较大腰围组高血压、高血脂、冠脉疾病及2型糖尿病发病率更高。
Dr. Kaplan says he does not know why obesity leads to sexual and urinary dysfunction, but he hypothesizes that vascular or blood flow changes to the pelvis, along with alterations in hormone levels due to obesity, may be the major culprit.
Kaplan博士表示肥胖为何导致性及泌尿功能障碍尚未知,但他提出假设——阴茎血流或血管的改变以及由于肥胖造成激素水平的变化可能为主要的原因。
"We now have an expanded understanding of how obesity can impact the health of men, and a simple way to recognize which men might be affected in these ways," Dr. Kaplan says. "This adds even more importance to the recommendation that men should maintain a healthy weight for their overall well-being."
“目前,我们扩展了对肥胖是怎样影响男性健康的认识,并且得到了一种简单易行的(测量)方法来判断哪些人可能会受到影响。”Kaplan博士指出,“男性为了整体健康而应该保持合适体重,而这(我们的研究)更增加了这项建议的重要性。”
纽约Presbyterian医院/ Weill Cornell医疗中心的研究人员称,随着男性腰围的增长,其可能更常出现性功能障碍及尿频。这篇发表于8月出版的不列颠国际泌尿学杂志的(BJUI)研究,首次全面显示了男性肥胖不仅对其心脏及代谢方面,还对其性及泌尿健康存在影响。
"The findings demonstrate that obesity in men -- part of a growing global epidemic -- affects their well-being in profound ways," says the study's senior investigator Dr. Steven A. Kaplan, the E. Darracott Vaughan Jr., Professor of Urology at Weill Cornell Medical College, director of the Iris Cantor Men's Health Center and chief of the Institute for Bladder and Prostate Health at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell.
纽约Presbyterian/Weill Cornel膀胱与前列腺健康研究所及Iris Cantor男性健康中心主任、Weill Cornell医学院泌尿科学教授小E. Darracott Vaugha以及本研究的高级研究员Steven A. Kaplan博士指出:“结果表明男性肥胖——作为增长中的全球流行病的一部分,在深层影响着他们的健康。”
"We have to think of the body in a much more holistic way. What we eat can have devastating consequences on more than just our hearts," Dr. Kaplan says. "Quality of life issues, such as sexual and voiding health, can be affected as well in drastic ways."
“我们不得不从一种更整体的角度思考机体。我们的所吃下的食物可能不仅仅对心脏产生破坏性的后果,”Kaplan博士指出,“生活质量方面,如性和排泄方面的健康,也有可能受到严重影响。”
The study also suggests that losing weight can help men overcome these issues that previously were not directly linked to body mass, Dr. Kaplan adds. In fact, additional findings conducted since this study was completed show that eliminating just 2.5 inches from the belly's circumference may lead to measurable improvement in sexual dysfunction and frequent urination, he says.
Kaplan博士补充,该研究还显示减肥可以帮助男性克服上述之前并不(认为)与体重直接相关的问题。事实上,该研究结束后的进一步(研究)结果显示,腹围仅减少2.5英寸就会使性功能障碍及尿频的情况获得显著的改善。”
The findings now offer physicians an easy metric to gauge which male patients might be experiencing sexual or urologic dysfunction, the researchers say.
研究人员称:已获得结果可以为医生提供一种简便的评价可能会有性或排尿障碍的男性患者的测量方法。
"Measuring a man's waistline is easy, noninvasive and does not require extensive testing," Dr. Kaplan says.
Kaplan博士说:“测量腰围简便、无创,并不需要繁琐的检查。”
Largest Waist Size Linked to Many Health Issues
最大腰围与许多健康问题相关
The research team studied 409 men diagnosed with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) at the Institute for Bladder and Prostate Health at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell. The goal of the study was to see if obesity was linked to LUTS, a common problem affecting older men. LUTS symptoms include difficulty urinating, such as increased frequency during the day and night. Previous smaller studies have suggested body weight could be linked to LUTS, but this new study was designed to be the most definitive and comprehensive to date, Dr. Kaplan says.
Of the participants enrolled in the study ranging from 40-91 years of age, 37.5 percent had a waist circumference of less than 36 inches, 33.5 percent of men had waists that were between 36-40 inches, and 29 percent of men had waists greater than 40 inches.
研究人员选取了409例来自于纽约Presbyterian/Weill Cornel膀胱与前列腺健康研究所的诊断为有下尿路症状的男性。研究目的为观察肥胖是否和经常困扰老年男性的下尿路症状相关。下尿路症状包括:排尿困难,如昼夜排尿次数增加。Kaplan博士称:之前小样本的已表明体重可能与下尿路症状相关,但本次则为迄今最确切和最广泛的研究。
The investigators found that a larger waist size was linked to more frequent urination: 39 percent of men with the biggest waistlines urinated more than eight times in 24 hours, compared to 27 percent of men in the middle range and 16 percent of men with the smallest waists. The same patterns were seen for nighttime urination: 44 percent of men with the biggest waists had to urinate more than twice at night, compared to 29 percent of men in the middle-sized group, and 15 percent of the slimmer men. The researchers also surveyed the participants about their sexual health and found that 74.5 percent of men with the largest waists reported erectile dysfunction, compared with 50 percent of men in the middle group and 32 percent of men with the smaller waists. Ejaculation problems followed the same pattern - 65 percent, 40 percent, and 21 percent, respectively.
研究人员发现腰围越大,尿频出现越多:最大腰围组的男性中39%(平均)24小时排尿8次以上,对比看来,这在中度腰围组有27%,最小腰围组仅为16%。在夜尿方面也有类似的情况:最大腰围组的男性中的44%出现夜尿两次以上,而这(仅)出现于29%的中度腰围组男性及15%的节食减肥者。研究人员还调查了研究对象的性健康情况并发现最大腰围组的男性中74.5%报告存在勃起障碍,对比中度及较小腰围组出现上诉情况的仅占各组的50%和32%。射精问题存在相似的情况,分别占各组的65%,40%及21%。
To provide a comprehensive view of health issues associated with waist circumference, the research team also assessed other variables linked to obesity. In the study, high blood pressure, cholesterol, coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes were more prevalent in men with larger waist sizes.
研究组还评估了与肥胖相关的其他变量,得出了与腰围相关健康问题的全面观点。在研究中,在较大腰围组高血压、高血脂、冠脉疾病及2型糖尿病发病率更高。
Dr. Kaplan says he does not know why obesity leads to sexual and urinary dysfunction, but he hypothesizes that vascular or blood flow changes to the pelvis, along with alterations in hormone levels due to obesity, may be the major culprit.
Kaplan博士表示肥胖为何导致性及泌尿功能障碍尚未知,但他提出假设——阴茎血流或血管的改变以及由于肥胖造成激素水平的变化可能为主要的原因。
"We now have an expanded understanding of how obesity can impact the health of men, and a simple way to recognize which men might be affected in these ways," Dr. Kaplan says. "This adds even more importance to the recommendation that men should maintain a healthy weight for their overall well-being."
“目前,我们扩展了对肥胖是怎样影响男性健康的认识,并且得到了一种简单易行的(测量)方法来判断哪些人可能会受到影响。”Kaplan博士指出,“男性为了整体健康而应该保持合适体重,而这(我们的研究)更增加了这项建议的重要性。”
上一篇:有三类“心病”最容 易引起ED
下一篇:早泄多是心理问题
论坛新帖
频道总排行
医学推广
频道本月排行
热门购物
评论排行
- 2011年临床执业医师考试实践技能真...(13)
- 腋臭手术视频(11)
- 2008年考研英语真题及参考答案(5)
- 节食挑食最伤女人的免疫系统(5)
- 核辐射的定义和单位(5)
- CKD患者Tm与IMT相关(5)
- 齐鲁医院普外科开展“喉返神经监护...(5)
- windows7激活工具WIN7 Activation v1.7(5)
- 正常微循环(5)
- 美大学性教育课来真的 男女上阵亲...(4)