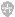【科普】图解为什么皮肤被蚊子咬后会痒痒?
2009-05-31 20:11:05 来源:丁香园 作者: 评论:0 点击:
A mosquito doesn't "bite," of course. Its proboscis works like a syringe to draw out blood. The resulting itch is caused not by the piercing proboscis or the protein in the mosquito's saliva but by the body's immune response to them.
当然,蚊子不“咬人”。它的口器工作原理就像注射器抽血。蚊子咬后刺痒的感觉不是由于其口器插入或蚊子唾液中的蛋白造成的而是我们对其的免疫反应产生的。
Less than 5 percent of skin is blood vessel, so when a mosquito comes for lunch, it has to fish. It casts its proboscis back and forth under the skin, sawing through tissue and probing in 10 second until it strikes a small blood vessel, or capillary.
皮肤中的血管少于5%, 因此当蚊子开始午餐时,它首先要“钓鱼”(挖一个通道)。它将口器在皮肤下来回抽插,来回锯组织并且每10秒插入组织一次直到它挖出一个小的血管或毛细管。
Saliva from the mosquito contains an anticoagulant to keep the blood from clotting so the mosquito can feed easily.
蚊子的唾液中含有一种抗凝剂以阻止血液凝固,这样蚊子很容易吸食血液。
To combat the foreign substance, the immune system releases a chemical called histamine. Histamine cause blood vessel near the bite to enlarge. This cause a wheal(a red, swollen area) to form on the skin. Histamine also irritates nerve ending in the skin and makes you itch.
为了抵抗这种外源性物质,免疫系统释放一种称为组胺的化学物质。组胺引起被咬部位周围血管扩张。这导致皮肤表面形成丘疹(一种红色的肿胀性区域)。组胺使皮肤中的神经末梢受激惹,从而使你感觉瘙痒。
The mosquito must pierce the epidermis, a thin upper layer of the skin made of several laryers of living cells topped by sheets of dead cells.
蚊子必须穿透表皮。表皮是皮肤上层由多层活细胞并覆以一层死细胞构成的皮肤上层。
Bundles of tough fibers that give the skin its elasticity, firmness and strength help make up the dermis. Blood vessels and nerves are here.
成束的纤维有助于皮肤具有弹性、坚固性以及韧性。血管和神经末梢正在此处。
Hair follicle: 毛囊
Hair bulb:毛球
Capillaries: 毛细血管
Nerve: 神经
Sweat gland: 汗腺
Hypodermis: Acts as an insulator and as a cushion.
皮下组织:具有隔热性以及缓冲作用

当然,蚊子不“咬人”。它的口器工作原理就像注射器抽血。蚊子咬后刺痒的感觉不是由于其口器插入或蚊子唾液中的蛋白造成的而是我们对其的免疫反应产生的。
Less than 5 percent of skin is blood vessel, so when a mosquito comes for lunch, it has to fish. It casts its proboscis back and forth under the skin, sawing through tissue and probing in 10 second until it strikes a small blood vessel, or capillary.
皮肤中的血管少于5%, 因此当蚊子开始午餐时,它首先要“钓鱼”(挖一个通道)。它将口器在皮肤下来回抽插,来回锯组织并且每10秒插入组织一次直到它挖出一个小的血管或毛细管。
Saliva from the mosquito contains an anticoagulant to keep the blood from clotting so the mosquito can feed easily.
蚊子的唾液中含有一种抗凝剂以阻止血液凝固,这样蚊子很容易吸食血液。
To combat the foreign substance, the immune system releases a chemical called histamine. Histamine cause blood vessel near the bite to enlarge. This cause a wheal(a red, swollen area) to form on the skin. Histamine also irritates nerve ending in the skin and makes you itch.
为了抵抗这种外源性物质,免疫系统释放一种称为组胺的化学物质。组胺引起被咬部位周围血管扩张。这导致皮肤表面形成丘疹(一种红色的肿胀性区域)。组胺使皮肤中的神经末梢受激惹,从而使你感觉瘙痒。
The mosquito must pierce the epidermis, a thin upper layer of the skin made of several laryers of living cells topped by sheets of dead cells.
蚊子必须穿透表皮。表皮是皮肤上层由多层活细胞并覆以一层死细胞构成的皮肤上层。
Bundles of tough fibers that give the skin its elasticity, firmness and strength help make up the dermis. Blood vessels and nerves are here.
成束的纤维有助于皮肤具有弹性、坚固性以及韧性。血管和神经末梢正在此处。
Hair follicle: 毛囊
Hair bulb:毛球
Capillaries: 毛细血管
Nerve: 神经
Sweat gland: 汗腺
Hypodermis: Acts as an insulator and as a cushion.
皮下组织:具有隔热性以及缓冲作用

相关热词搜索:蚊子
上一篇:中国专家研制抗疟疾药品获世界级大奖
下一篇:住院医师培训计划令越来越多年轻医生变得歇斯底里
论坛新帖
频道总排行
医学推广
频道本月排行
热门购物
评论排行
- 2011年临床执业医师考试实践技能真...(13)
- 腋臭手术视频(11)
- 2008年考研英语真题及参考答案(5)
- 节食挑食最伤女人的免疫系统(5)
- 核辐射的定义和单位(5)
- CKD患者Tm与IMT相关(5)
- 齐鲁医院普外科开展“喉返神经监护...(5)
- windows7激活工具WIN7 Activation v1.7(5)
- 正常微循环(5)
- 美大学性教育课来真的 男女上阵亲...(4)